The Power of Vibrant Green Leaves! Kale Benefits & Calories: A Low-Calorie Nutritional Powerhouse
Through ‘The Power of Vibrant Green Leaves! Kale Benefits & Calories: A Low-Calorie Nutritional Powerhouse’ post, we will explore kale’s benefits, nutritional content, calories, seasonal availability, selection tips, and storage methodsin detail.
If we were to describe kale in one sentence:
“A low-calorie superfood with vibrant green leaves.”
Kale was first cultivated about 2,000 years ago in ancient Rome and Greece and is now loved as a superfood around the world. In Europe, kale thrived even in cold climates, making it a staple winter vegetable. During the Middle Ages, it was an essential food for farmers. During World War II, when the British faced food shortages, kale grew easily with minimal care and provided essential vitamins and minerals, greatly aiding the nation’s nutrition. Recently, endorsements from Hollywood celebrities and health experts have further boosted its popularity as a superfood. Kale is praised not only for its unique appearance but also for being low in calories and high in nutrients, making it ideal for health and weight management.
This post covers kale’s benefits, nutritional content, seasonal availability, selection tips, and storage methodswith easy-to-understand diagrams and tables.
Let’s get started!
- Kale Benefits
1. Antioxidant Properties

* Kale contains antioxidants such as Vitamin C, Beta-carotene, Quercetin, and Kaempferol, which neutralize harmful free radicals, preventing damage to cells and DNA.
※ Vitamin C: Water-soluble antioxidant.
– Neutralizes free radicals in watery environments inside and outside cells.
– Prevents oxidative damage to proteins and DNA.
※ Beta-carotene: Fat-soluble antioxidant.
– Removes free radicals in fat-rich areas like cell membranes.
※ Quercetin & Kaempferol: Flavonoids with strong antioxidant properties.
– Activate antioxidant enzymes and reduce oxidative stress in cells.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects

* Vitamin K, Alpha-linolenic Acid, Quercetin, and Kaempferol help reduce and regulate inflammation, preventing inflammatory diseases.
※ Vitamin K
– Inhibits the NF-kB signaling pathway, reducing inflammation.
– Lowers levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a key inflammation marker.
※ Alpha-linolenic Acid: Omega-3 fatty acid.
– Converts to EPA and DHA, which inhibit inflammatory substances.
– Reduces inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins.
– Promotes anti-inflammatory cytokine production.
※ Quercetin & Kaempferol
– Inhibit COX-2 enzyme responsible for prostaglandin production.
– Help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
※ Prostaglandins: Substances that cause inflammation and pain.
3. Joint Health Improvement

* The abundant Vitamin K in kale plays an essential role in bone and cartilage formation, reducing joint damage. Vitamin C promotes collagen synthesis, protecting cartilage and enhancing its cushioning function. Additionally, Quercetin and Kaempferol inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators like cytokines and prostaglandins, helping reduce joint inflammation.
※ Vitamin K: Activates osteocalcin protein.
– Osteocalcin: A protein essential for bone formation and maintenance, helping calcium bind properly to bones and cartilage.
– Facilitates calcium deposition in joint cartilage, reducing cartilage damage and helping prevent joint diseases like arthritis.
※ Vitamin C
– Plays a vital role in synthesizing collagen, a key component of joint cartilage.
– Helps prevent cartilage damage and wear, maintaining joint function and relieving pain.
※ Quercetin & Kaempferol
– Inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators like cytokines and prostaglandins, reducing joint inflammation.
– Help relieve pain and reduce joint damage in patients with inflammatory arthritis.
4. Heart Health Improvement

* Kale’s abundant soluble fiber inhibits cholesterol absorption in the intestines, while Vitamin C and Beta-carotene prevent LDL cholesterol oxidation, helping prevent the formation of plaques (fat deposits) in the blood vessels. Additionally, potassium helps dilate blood vessels, facilitating blood flow and naturally lowering blood pressure.
※ Soluble Fiber : Inhibits cholesterol absorption in the intestines and promotes its excretion.
※ Vitamin C & Beta-carotene: Antioxidants
– Prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol).
– Help prevent the formation of plaques(fat deposits) in blood vessels.
– Protect blood vessels and prevent atherosclerosis through antioxidant action.
※ Potassium
– Balances sodium levels to regulate blood pressure.
– Dilates blood vessels and facilitates blood flow, naturally stabilizing blood pressure.
5. Eye Health Protection

* The abundant lutein and zeaxanthin in kale are concentrated in the macula, helping protect the retina and reduce oxidative stress caused by UV rays, thereby supporting eye health. Additionally, beta-carotene is converted to Vitamin A in the body, which plays a crucial role in maintaining vision.
※ Lutein & Zeaxanthin: Powerful antioxidant carotenoids
– Concentrated in the macula, located in the center of the retina.
– Reduce oxidative stress caused by blue light and UV rays, protecting vision and eye cells.
– Help prevent macular degeneration.
※ Beta-carotene: Converts to Vitamin A in the body
– Vitamin A: A component of the visual pigment rhodopsin; a deficiency can lead to night blindness.
– Rhodopsin: Essential for vision in low-light conditions.
6. Other Benefits

* Other Benefits: Bone health, detoxification, cancer prevention, weight management, digestive health, immunity boost, blood sugar control, etc.
※ Bone Health: High in calcium and Vitamin K, which support bone density.
※ Detoxification: Glucosinolates activate liver detox enzymes.
※ Cancer Prevention: Contains glucosinolates and isothiocyanates that inhibit cancer cell growth.
※ Weight Management: Low in calories and high in fiber, increasing satiety.
※ Digestive Health: Fiber supports gut health and prevents constipation.
※ Immunity Boost: Vitamin C enhances immune cell function.
※ Blood Sugar Control: Fiber helps prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Kale Nutritional Content & Calories

* Calories per 100g: 35 kcal.
* Kale is a low-calorie, nutrient-dense superfood rich in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Kale’s Seasonal Availability

※ Season: October to February
※ Kale thrives in cold weather, making it a winter vegetable.
– Tip: Kale harvested after the first frost is sweeter and more tender.
- How to Select Kale
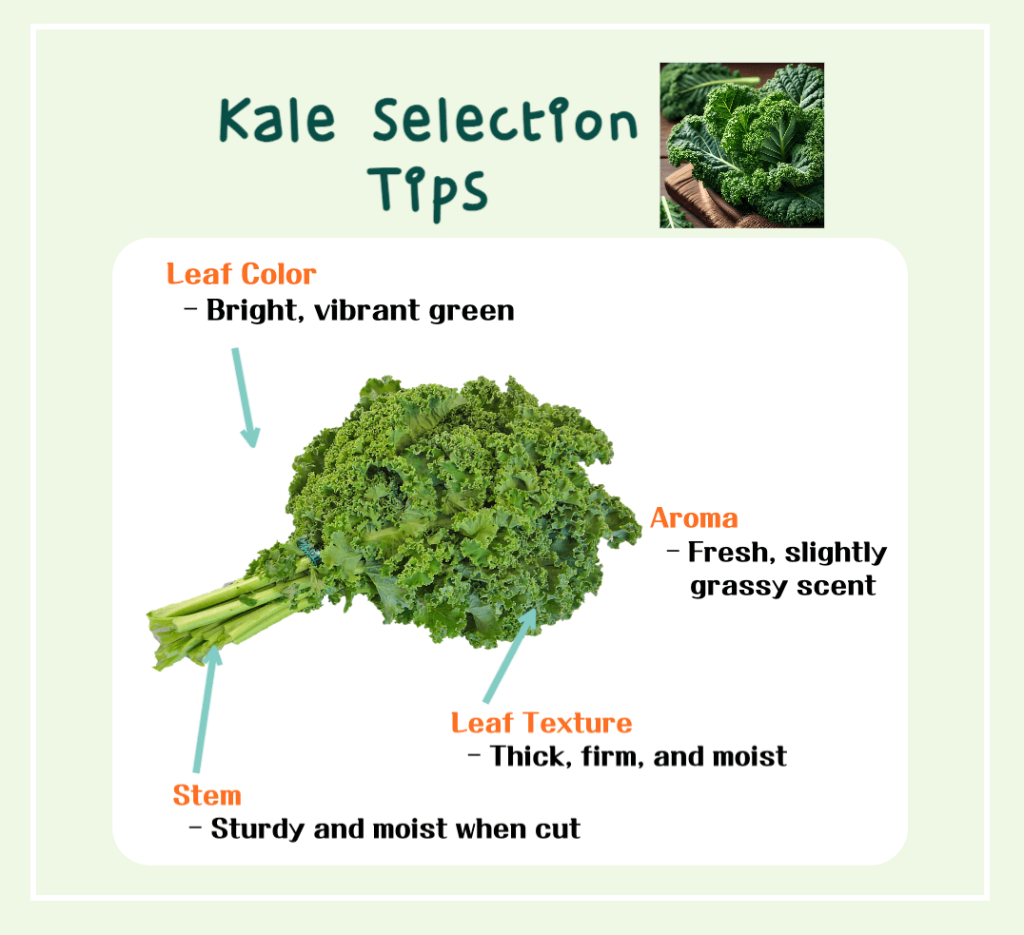
* Color: Choose vibrant green leaves.
* Texture: Leaves should be thick, firm, and moist.
* Shape & Size: Select evenly shaped leaves.
* Stems: Stems should be thick and fresh.
* Aroma: Fresh kale has a grassy scent.
- How to Store Kale & Precautions
1. Storage Methods
* Refrigeration(5-7 days)
– Do not wash before storing. Wrap in paper towels and seal in a bag.
* Freezing(Up to 6 months)
– Blanch, cool, and freeze in airtight containers.
2. Precautions
* Avoid Excess Moisture: Prevents wilting and mold.
* Minimize Air Exposure: Store in sealed containers.
* Low Temperature: Always refrigerate or freeze.
* Remove Damaged Leaves: To prevent spoilage.
Conclusion
We’ve covered kale’s benefits, nutritional content, calories, seasonal availability, selection tips, and storage methodsin detail. We hope this post helps you understand kale better!
If you need further assistance or more translations, feel free to ask!
It would be great to also check the calorie information for various foods.
Thank you for reading!